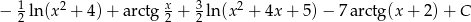Zadanie nr 9191177
Oblicz całkę 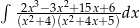 .
.
Rozwiązanie
Mianownik jest iloczynem dwóch nierozkładalnych czynników kwadratowych, zatem funkcja podcałkowa jest sumą dwóch ułamków prostych drugiego rodzaju.
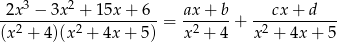
Mnożąc obie strony przez mianownik lewej strony mamy
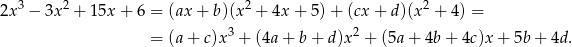
Porównując współczynniki przy kolejnych potęgach  otrzymujemy układ równań
otrzymujemy układ równań
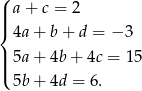
Podstawiając 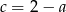 do trzeciego równania mamy układ
do trzeciego równania mamy układ
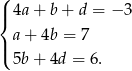
Wstawiamy teraz 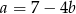 do pierwszego równania.
do pierwszego równania.
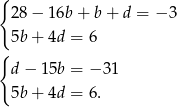
Podstawiamy teraz 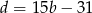 do drugiego równania.
do drugiego równania.
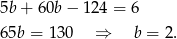
Zatem 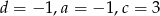 oraz
oraz
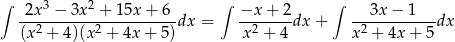
Całkujemy ułamki proste
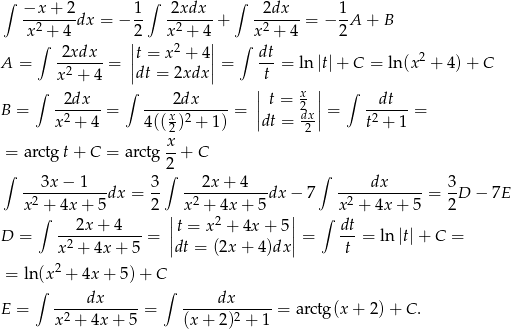
Mamy więc
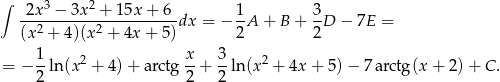
Odpowiedź: